Institutional Distinctiveness
Institutionalization of Indigenous literary Intellectual Property Rights for Operational Excellence
The highest form of educational scholarship is ‘Scholarship of Discovery’. Every functional unit of the DMIHER contribute towards generation of new literary ideas. Every literary innovative concept is piloted, evaluated and subsequently Institutionalized as a best practice that form the basis of Evidence based education at the University. Peer review of such ideas has generated a sizable number of Literary IPRs which are subsequently Institutionalized. The IPR unit of R&D cell of the University is central towards mentoring and hand holding for ideation, conceptualization and copyright applications. Over last five years , number of copyright applications shows an incremental growth. Generation of IPRs is one of the developmental indicators in University’s Perspective Development Plan. The various faculty contributions towards generation of new ideas is as depicted in Fig 1 :
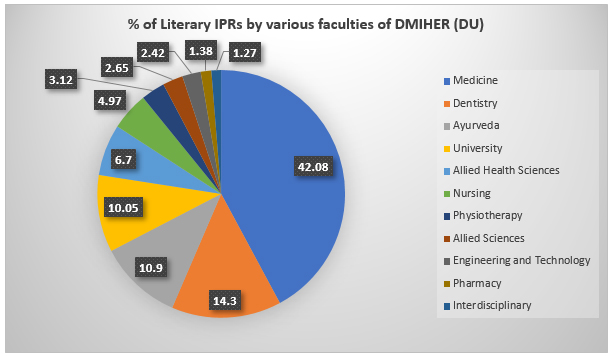
Literary IPRs registered fall within the category of Learning Resource Material, Curricular transactions, Educational Innovations, Clinical Protocols, Models & Modules , Concept papers, Examination reforms, Technology based Innovations, SOPS, Quality reforms and Emerging areas of knowledge. The total number of IPRs generated are 865, segregated into various categories as shown in Fig : 2
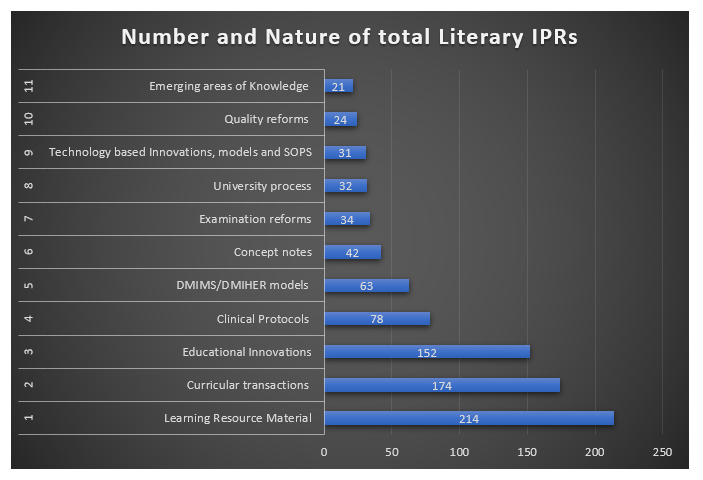
Fig 2 : Number and Nature of Literary copyrights generated in last five years
There are two structured mechanisms for Institutionalization of in-house Literary IPRs; 1. Innovation to Institutionalization and 2. Institutionalized mechanisms generating Innovations
Mechanism 1 : Innovation to Institutionalization
- Ideation of theme
- Submission to School of Higher education & Research for validation of idea
- Piloting the innovation at workplace
- Refining idea in terms educational principles, evidence , relevance and feasibility
- Submission of innovation manuscript to IPR cell of R&D.
- Review of innovation at IPR cell and subsequent application to Copyright office, GOI.
- Registered of literary IPR
- Institutionalization of the literary IPR
- Sharing/Publication of pilot study of registered IPR at various scientific forums for peer review
Mechanism 2 : Institutionalized mechanisms generating Innovations
- Ideas emanating out of Institutionalized practices, generally as a result of midterm evaluations
- Submission to School of Higher education & Research for validation of idea
- Pilot study of the innovative idea
- The results published and / or presented in scientific forum for peer review
- The idea refined based on peer review
- Submission of innovation manuscript to IPR cell of R&D
- Application of the innovation by IPR cell to Copyright office, GOI
- Further refining of Institutionalization practice.
Every registered literary IPR resonates NAAC Core Values and Criteria as depicted in Table 1 & Fig 3:
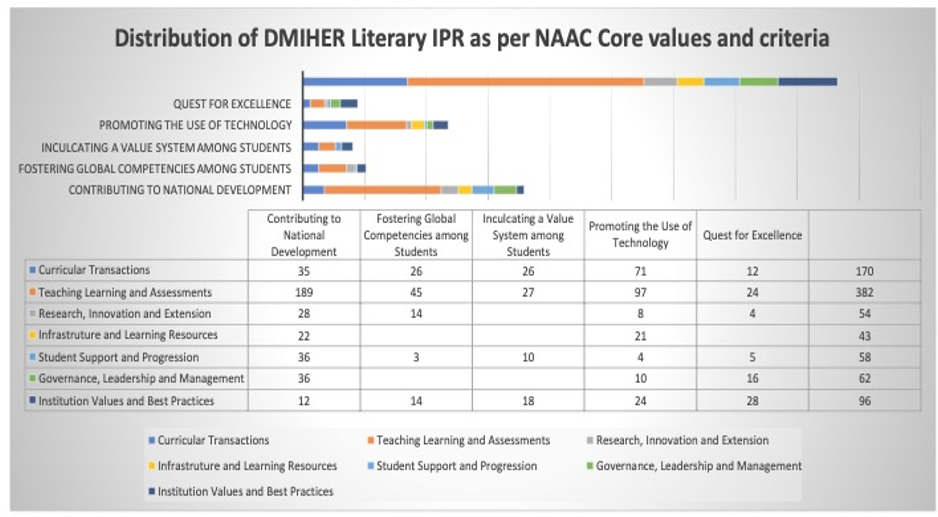
Fig 3 : Institutional Literary copyrights aligned to NAAC Core Values and Criteria
Impact : A total of 306 (35%) indigenous literary IPRs are Institutionalized till date. The various Academic and Administrative functioning of University that have been impacted by Institutionalizing registered IPRs are as follows;
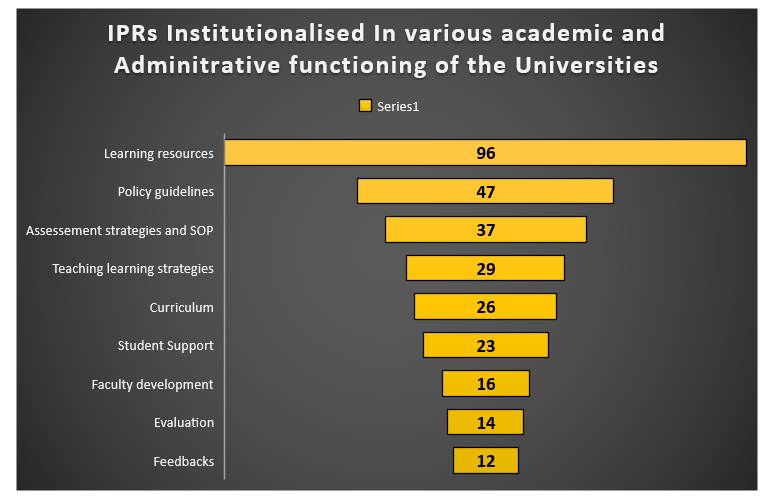
Fig 4 : Few significant Institutionalized indigenous Literary IPRs
Teaching Learning :
- Hi Tech Hi touch model of Competency Based Dental Education
- Interactive Intragroup tutorials
- Structured & Standardized LRM
- Modified Problem Based Learning
- The DMIMS Nine step working Model of simulated case-based clinical Skill training and assessment
- SOP for Clinical/Practical Skill Training through Hybrid Protocol Simulations and Standardized Patients
- Critical self thinking inventory for clinical examination
- The DMIMS Nine Step Working Model of Simulated Case Based Clinical Skill Training And Assessment
- ‘Seven pronged blended Learning model for Indian Medical Graduate’ L-95175/2020, is a jointly authored IPR by DMIHER, Wardha, SRIHER, Chennai MUHS, Nasik, KUHS, Kerala and Pt BD Sharma UHS , Rohtak
- Reverse Objective Structured Clinical Examination (OSCE)
- Primary & Secondary Test Blueprints
- DMIMS Scheme for Formative Medical Classroom
- DMIMS Referral Document for valuation of answer sheets
- Learner led validation of outcome based electronic question bank
- OSCE-OSPE Bank: A synergistic approach for Health Professions Education
- Formative Assessment for Post Graduates in Medical Education – A Strategic Initiative towards CBE
- Structured Comprehensive Assessment of Competency
- Model of compensation for repetition of MCQ’s or Internal options in Examinations
- Midpoint appraisal of the Summative Examination process
- DMIMS modified customized answer sheet with contingent page
- DMIMS model of competency based assessment framework for theory examinations
B. Student support :
- HEART initiative for Rapid Learners
- Marathi to English Dictionary for Medical Students
- ‘PPP Questionnaire’ – A tool to assess Learning behaviour in adolescent & adult learners
- Early Research Exposure Model” for Medical Undergraduates
- DMIMS Research and Publication Model For Undergraduate Competency Based Medical Education
- Value Education for First year Students – Inculcation Course & Third year Students – Consolidation Course
- Yoga a way of life : Unique Yogic Module For Better Health
- Curricular revision model for all academic programs
- DMIMS 4 Step Escalating Outcome Based Education Model for Health Sciences Education
- Academic Appraisal program
- CBCS in Undergraduate Medical Education
- Attitude, Ethics and Communication module for 1st Professionals
- Symbiosis Interdepartmental Scientific Activity and Interdepartmental Case Discussion as Contextual TL Tools
- Credit framework for various programs under DMIMS
- Academic Administrative Audit: The DMIMS Model
- A Novel Model using PPP approach to cater health needs of Tribal populace & Forest dwellers in Vidarbha region of Maharashtra.
- Strategic planning and preparation of Perspective Development Plan :The DMIMS ten step guide
- SOP for e-assignments, e practical discussions, e attendance as part of e academic teaching learning process,
- Utility Document for Paramarsh Mentee Institutions under DMIMS
- Evaluation Blueprint of a Faculty development program
- Absolute Learning Gain: For Program Output towards FDP for Health Professionals
- DMIMS Model Of Outcome Based Continuous Professional Development Initiatives
Institutionalization of Indigenous literary Intellectual property rights for operational excellences thus distinctive in its systematic integration for academic and administrative matters of the University that corroborates its commitment to Quality benchmarks in field of Higher Education.
